Here are the strategies to master AI prompting for technical writers. This article will show you how AI can transform your workflow, freeing you to focus on the complexities of your subject matter.
Recently I’ve been helping my younger brother figure out the necessary components he needs for his gaming PC. Annoyingly he asks questions like “So, like, what’s the BEST graphics card? Can you get me the one with the most RGB lights?” or “Can we get the fastest RAM ever? Will it make my games load instantly?”.
This moment is when I began to realize that explaining something to a younger sibling can be a humbling experience. It’s a point in time when you become aware of the wisdom you hold, the years of firsthand experience you’ve gained, and the importance of using simple language to explain complex topics effectively.
In the same respect technical writers have to pretend like they’re writing for someone who has no prior knowledge of the topic they’re writing about. They have to make complicated language sound simple, and while it may be as humbling as talking to a younger sibling, this is harder than it seems. The good news is this is where AI can be of help.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the top five strategies for master AI prompting for technical writers to understand how AI can specifically benefit them.
Introduction to AI and Prompt Engineering
Before delving into the strategies, let’s first understand what AI prompt engineering is and why it’s important in technical writing.
AI prompt engineering involves creating specific and detailed instructions that guide AI in generating outputs that best suit your requirements. For technical writers, this includes designing prompts that help them create clearer and more audience-specific content.
The fusion of AI and technical writing enhances content creation efficiency. No more staring at a blank page or struggling with writer’s block. AI prompt engineering opens up a machine’s potential to create solid starting points for your technical content.
Understanding prompt engineering in detail can be challenging for some. It’s worth exploring more about this concept through IBM, a leading IT company, to gain insights on prompt engineering.
Check it out here:

The Value of AI in Technical Writing
AI tools are not here to replace us but to empower us. With the growing demand for technical documentation across industries, AI has become a force multiplier, enabling writers to be more productive, accurate, and consistent in their work.
The key here is to harness the right tools and techniques to maximize this symbiotic relationship between human intellect and machine efficiency. This is where our journey with prompt engineering comes in.
In Case You’re New to Prompt Engineering
AI prompt engineering involves creating specific and detailed instructions that guide AI in generating outputs that best suit your requirements. For technical writers, this includes designing prompts that help them create clearer and more audience-specific content.
Technical writers who have mastered this art form can significantly increase their output and maintain a high level of quality, saving valuable time and effort.
Like riding a bike, trying things for the first time can be intimidating. It can take a certain amount of trial and error to find your balance and footing. Just in case you want to dive deeper can I suggest this free introductory course by Dr. Jules White of Vanderbilt University to get you started (although unsolicited, I must say I really liked Dr. White’s course. Just to be clear, I’m not getting any commission for recommending it).
Top 5 Prompt Engineering Strategies for Technical Writers
Now that we have that out of the way, here are the top 10 strategies technical writers can implement to become prompt engineering experts.
1. Understanding Language Models
Language models like OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 have transformed global communication with their impressive natural language processing skills. Their talent for engaging in human-like conversations has changed industries, from customer service bots to writing support.
To craft compelling prompts with these models, it’s crucial to explore their capabilities and limits. By checking AI developers’ guides, trying out sample prompts, and understanding how the models work, users can unlock the full power of these advanced language models for various uses.
ChatGPT was released a little over a year ago and it has had certain improvements and updates since. To have a really short overview of what it is and what it can do though you can head on over to this clip by Bernard Marr.
2.Focusing on Audience and Incorporating User Scenarios
Understanding your audience is crucial in prompt engineering, especially for technical writers. They need to anticipate user needs to craft relatable and user-friendly documentation. By integrating practical user scenarios, writers can address potential user questions and challenges, allowing AI to offer tailored solutions.
Effective technical content bridges the gap between technology and users by providing prompts that resonate with the audience’s context and difficulties. User scenarios play a vital role in technical writing, helping AI generate valuable content that meets end-user requirements through user-centric prompts.
3. Semantic Enrichment
This may sound complex at first, but it’s fairly simple. Semantic enrichment goes beyond dictionary definitions, it dives into the context that surrounds words. It uncovers the different shades of meaning, emotional connections, and cultural subtleties that enhance language.
For example, “red” can represent a blazing sunset, a cautionary stop sign, or a lover’s flushed cheeks. The purpose of semantic enrichment in prompt engineering is to pinpoint what “red” exactly means.
Tips on how to add semantics:
- Use domain-specific vocabulary to align the AI’s tone with the subject matter.
- Explicitly state the desired structure for a logically organized response.
- Incorporate examples or analogies to clarify complex concepts.
It’s not as hard as it sounds, honestly; it’s as simple as making an omelette!
Here’s a sample prompt input:

Why is the sample prompt successful?
- It uses culinary-specific terms such as “whisk,” “non-stick skillet,” and “emulsify,” aligning the AI’s tone with cooking terminology.
- The request for a structured explanation in “three main steps” organizes the information logically, making it easier to follow.
- Comparing the gentle folding of eggs in a skillet to “painting on a canvas” provides a vivid, easy-to-understand analogy for beginners, helping to clarify the technique involved in making a French omelette.
Here’s the output:

Why is the output successful?
- Clear structure: Three main sections—preparing eggs, cooking omelette, serving—make it easy to follow.
- Culinary terms: Inclusion of terms like “whisk,” “non-stick skillet,” and “emulsify” adds authenticity and clarity.
- Visual analogy: Using a canvas painting analogy simplifies the technique, aiding understanding.
- Step-by-step: Clear explanation from cracking eggs to serving ensures understanding and success.
- Texture and presentation: Emphasis on achieving creamy texture, avoiding browning, and suggesting garnishes for flavor and aesthetics.
3. Variety in Prompt Styles
Just as AI models recognize the importance of diverse training data, they also benefit from a variety of prompt styles. Don’t settle for a uniform approach to prompts. Experiment with various structures, question types, and tones to build a versatile prompt toolbox.
In experimenting with different prompt styles we first have to master the basics of prompting before moving forward towards more advanced tactics or actual styles of prompting.
Mastering the Basics:
- Speak clearly: Use technical terms as needed, but avoid jargon for better AI understanding.
- Get to the point: Be concise to help the AI focus on your main request.
- Define the AI’s role: Clearly outline the AI’s task and the expected outcome for effective responses.
- Provide examples: Offer both positive and negative examples to guide the AI accurately.
Unlocking Advanced Tactics/Actual Styles:
- Specify input & output: Clearly state the information you want the AI to use and the response format, like a script.
- Use zero-shot prompting: Giving a general directive to the AI to prompt varied responses, enabling the tool to produce a diverse range of answers.
- Enhance with one-shot prompting: Similar to zero-shot prompting but adding more context to improve results and help the AI generate better responses.
- Guide chain-of-thought prompting: Basically, its you allowing AI to continually learn from your prompts as you walk it through the process of how you thought of and dissected the problem that you are currently trying to solve.
This list allows you to explore different prompt styles and see what works best for you or for the problem that you are looking to solve.
4. Iterative Improvement
AI prompt engineering requires practice and ongoing refinement, much like any skill. When exploring prompts and evaluating AI-generated content, take note of successful strategies and areas for improvement. Through an iterative process in prompt design, you can progressively enhance the quality and effectiveness of your writing.
Don’t think of it as a puzzle where each piece has to fit perfectly with the rest of the pieces. Instead, look at it more like Chess wherein there are different iterations of strategies to win the game, while at the same time needing to refine and create a new strategy at the brink of losing.
The same goal exists though to eat the King or in this case, create a successful prompt in order to meet the desired output for your written work as a technical writer. The only difference is that you and AI are on the same side.
To get a clearer demonstration of how iterative improvement works with regard to AI prompting here is an example of AI being prompted to tell a joke.
Initial Prompt: “Tell me a joke”
Instruction: Ask the AI for a specific type of joke, such as a pun or a knock-knock joke.
Iteration 1: ” Could you please tell me a pun?”
Instruction: Provide a topic or theme to the AI to generate a joke related to that topic, such as animals, food, or technology.
Iteration 2: “I’m in the mood for a joke about food. Can you cook up something funny?”
Instruction: Experiment with adding additional context or setting for the joke, such as asking for a joke suitable for telling at a party or in a professional setting.
Iteration 3: “Imagine I’m at a party, and I need a joke to break the ice. Give me your best party joke!”
Instruction: Reflect on the jokes generated by the AI and note which ones received the best response. Use this feedback to refine future prompts for more enjoyable and entertaining joke generation.
Iteration 4: “Reflecting on the jokes you’ve shared, let’s try something a bit different. How about a joke suitable for sharing in a professional setting?”
Each iteration refines the prompt to guide the AI toward generating a more specific type of joke, resulting in a more tailored and enjoyable experience.
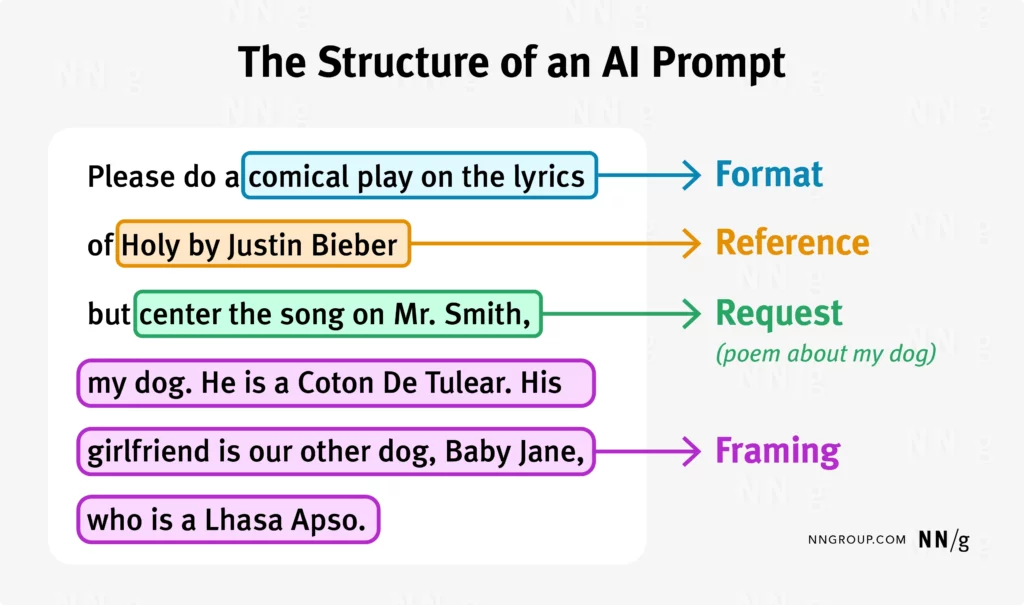
5.AI Prompt Structure
Mastering the structure of an AI prompt is crucial for technical writers looking to fully utilize AI tools. According to NNGroup, most prompts ask for information or action, influencing how AI responds based on language, specificity, and context. This highlights the importance of a clear prompt structure for precise AI outputs. Crafting well-structured prompts helps steer AI towards desired outcomes and enhances audience engagement. A well-crafted prompt serves as a link between human intent and machine response, improving communication and achieving writing goals effectively.
Here is a snapshot of the AI Prompt Structure that the Nielsen Norman Group highlighted.
Also Read: AI Prompts for Business Writing
Reading through all these strategies are foundational in your journey of mastering AI prompting as a technical writer, but first-hand experience will always be the greatest teacher!

To get you started on your own here are 50+ AI Technical Writing Prompts shared by Joshua Gene Fechter the founder of Technical Writer HQ and Squibler (a writing software).
Key Takeaways
- Master AI prompt engineering to boost a technical writer’s efficiency.
- Tailor prompts to meet audience needs using real user scenarios.
- Enhance content with semantic enrichment for clear language usage.
- Experiment with varied prompt techniques for improved AI-generated results.
- Understanding an AI prompt’s structure leads to a well-crafted prompt that bridges human intent and machine interpretation.
What’s Next?
The future of technical writing is intertwined with AI. As technologies advance, they will provide technical writers with opportunities to excel in their craft and serve their audiences effectively. By mastering prompt engineering, you place yourself at the forefront of innovation, prepared to lead in the era of AI-driven technical communication.